Analyzing RedLine
Overview
RedLine is an infostealer that steals credentials from a variety of applications, including Chrome, Discord, and Steam. It is often distributed through pirated software or by impersonating official download sites of popular executables.
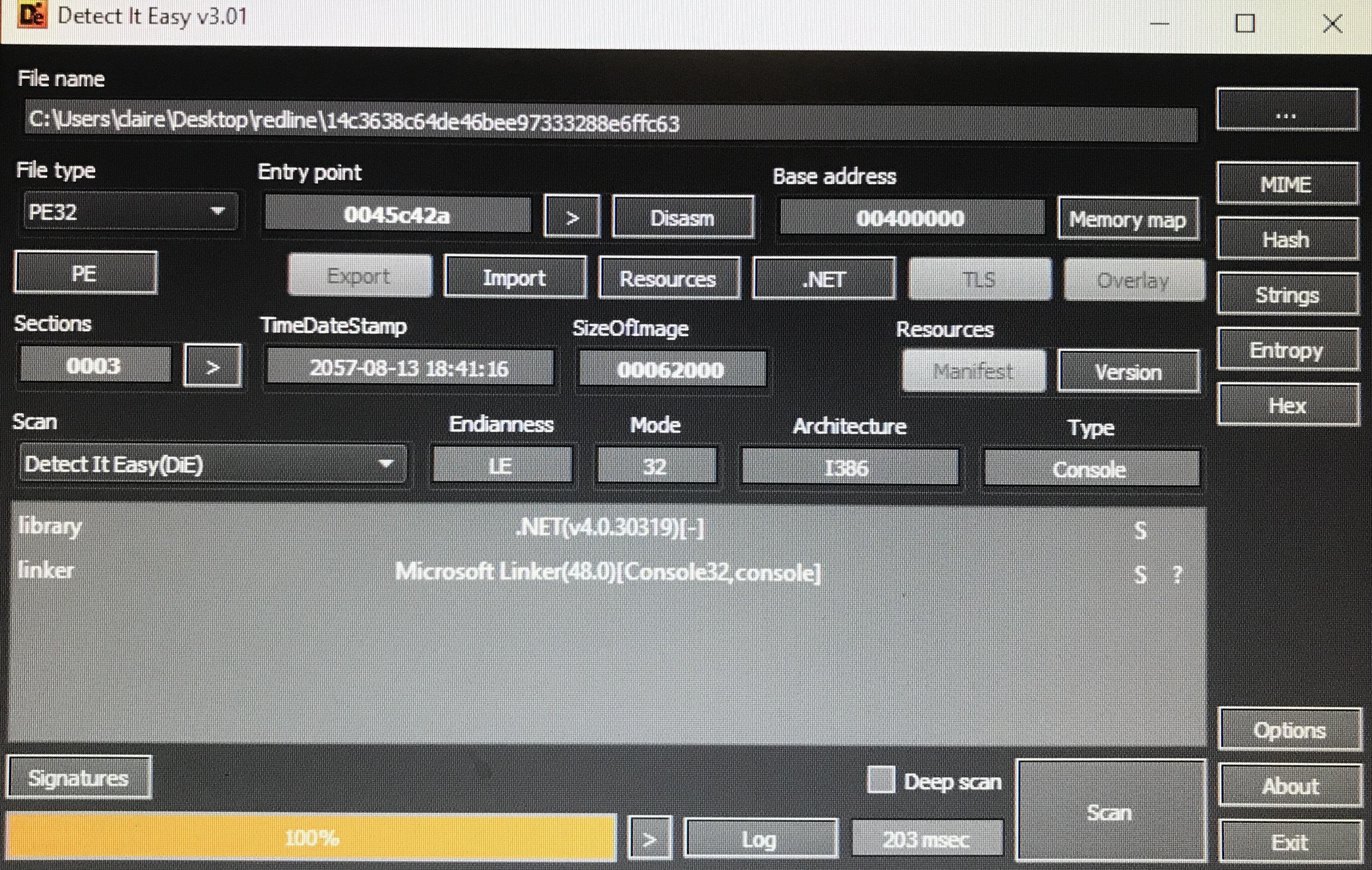
I obtained two samples of RedLine from vx-underground: one with MD5 hash 14c3638c64de46bee97333288e6ffc63 and original name Wheal.exe, and one with MD5 hash e307bef30d37b965e01405176a9e30fe and original name Swaling.exe. The program is a 32-bit .NET executable.
The First Stage
Looking at the executable in dnSpy, we find that the names of all functions have been obfuscated. Wheal.exe appears to choose random words used in system functions for its names:
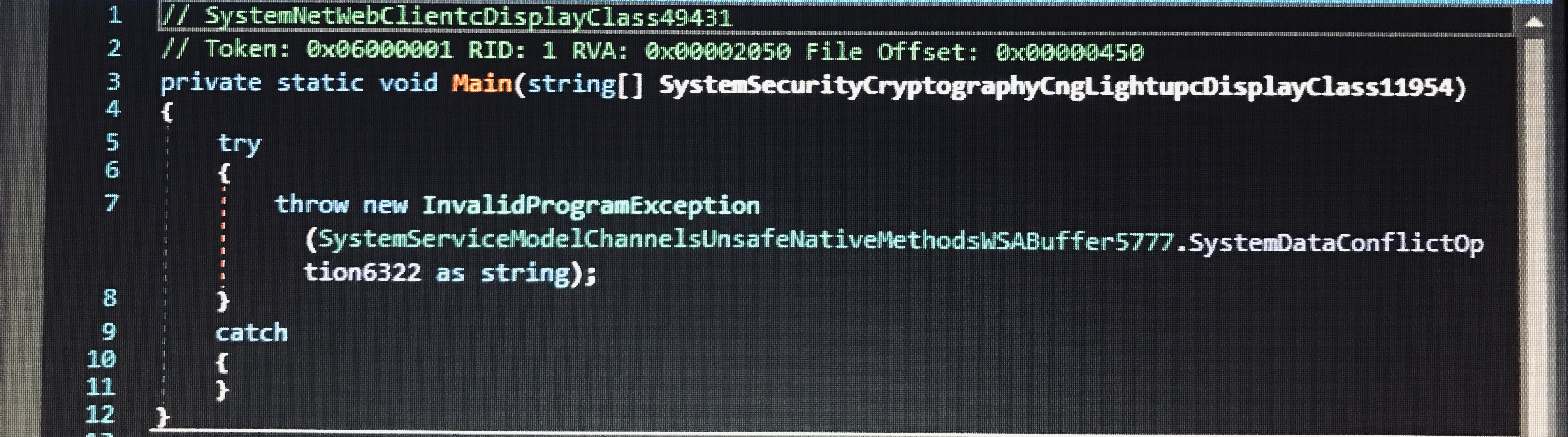
Swaling.exe names functions using a similar string of words, but each word is reversed:
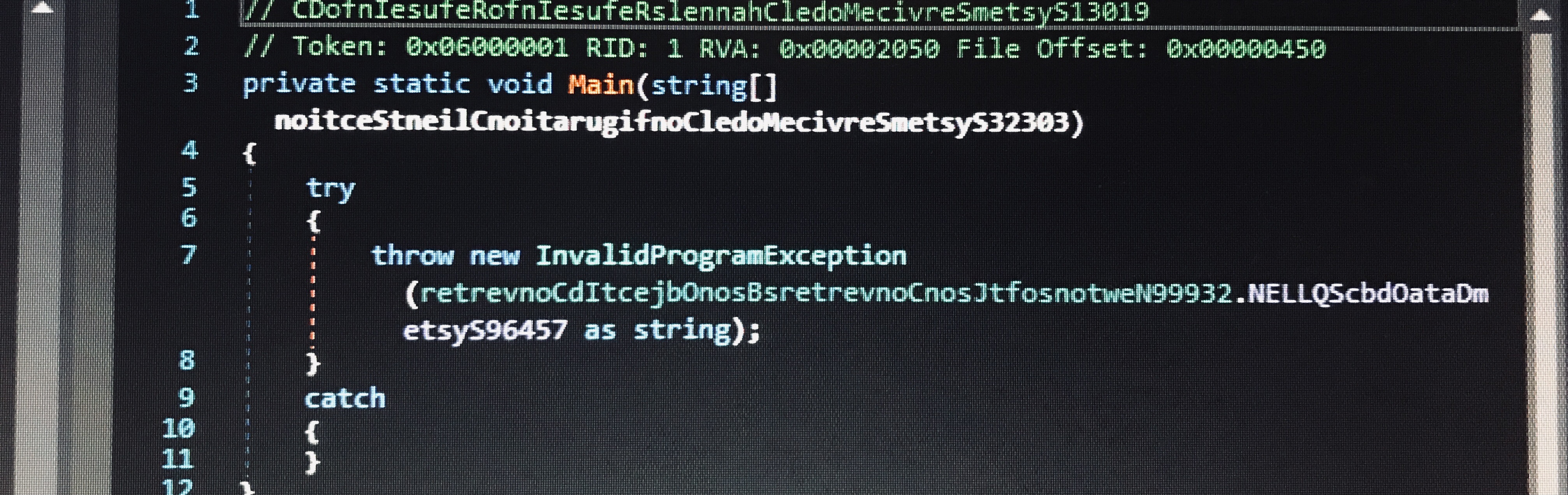
Looking through the functions, a long string immediately stands out. The string NetUnsafeNclNativeMethodsHttpApiTOKENBINDINGRESULTDATAV3408 is a garbage value that gets inserted into most of the strings in this program. Removing it, we are left with valid base64. This decodes to another base64 string, which in turn can be decoded to produce another .NET executable.
The Second Stage
At this point, I focused my attention on the executable decoded from the base64. This program is much less obfuscated than the initial dropper. With descriptive names like ScanPasswords and GetTokens, we’re very quickly able to get an idea of the sample’s capabilities.
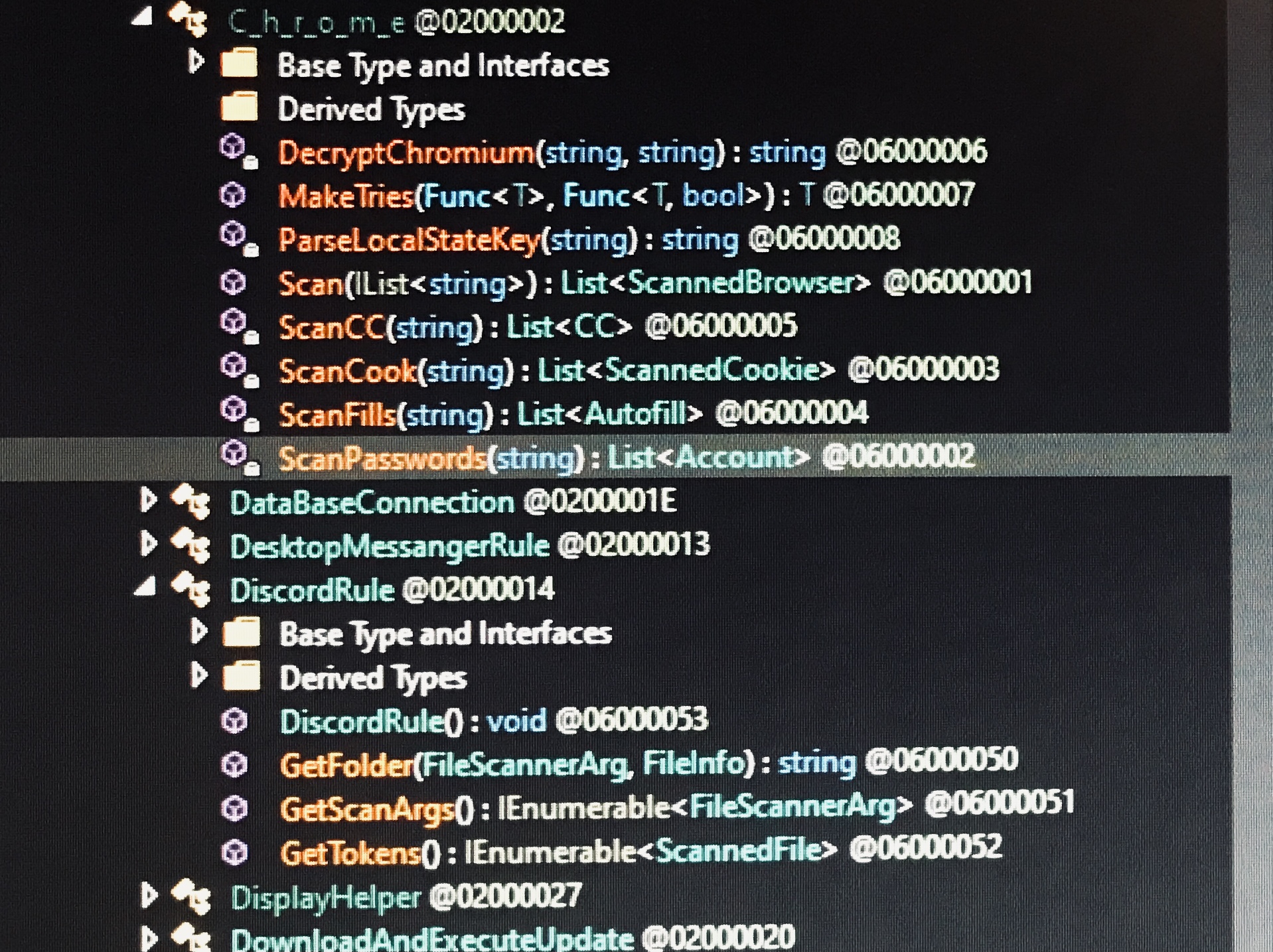
Notable class names include AllWalletsRule, ArmoryRule, BrowserExtensionsRule, C_h_r_o_m_e, CoinomiRule, DesktopMessangerRule, DiscordRule, ElectrumRule, EthRule, ExodusRule, GameLauncherRule, GuardaRule, NordApp, OpenVPNRule, andProtonVPNRule. This reveals that the program is designed to steal sensitive data, including cryptocurrency wallets and autofilled browser credentials.
Several strings are obfuscated by inserting garbage characters, then removing them with a simple find and replace. Other than this, there is very little obfuscation.
Initialization
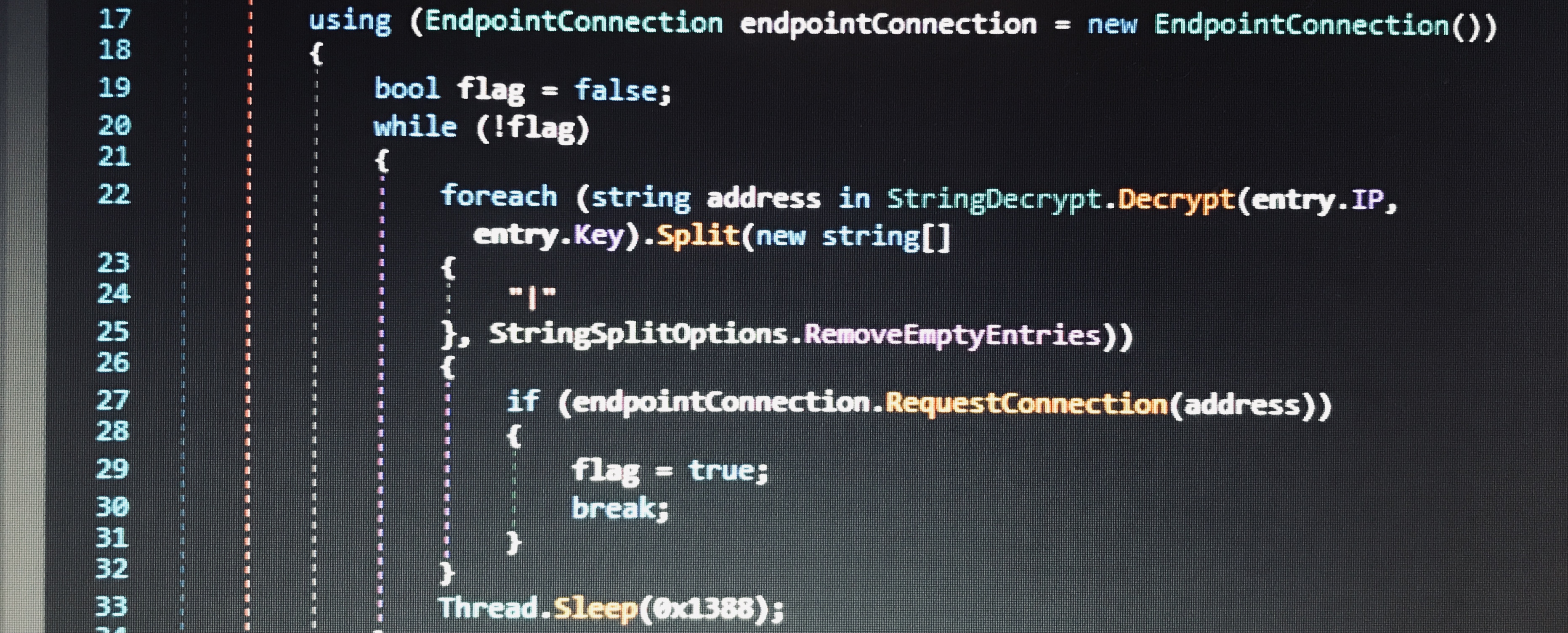
The entry point contains a class with members IP, ID, Message, and Key. IP and ID are base64-encoded data, and Message and Key are plain text. These parameters likely provide a unique identifier for each copy of the program. Once IP and ID are base64-decoded, they can be XORed with the value of Message in order to obtain a domain and a username respectively.
It appears that the IP parameter can sometimes contain multiple domains separated by |. The program attempts to create a connection to all IPs listed.
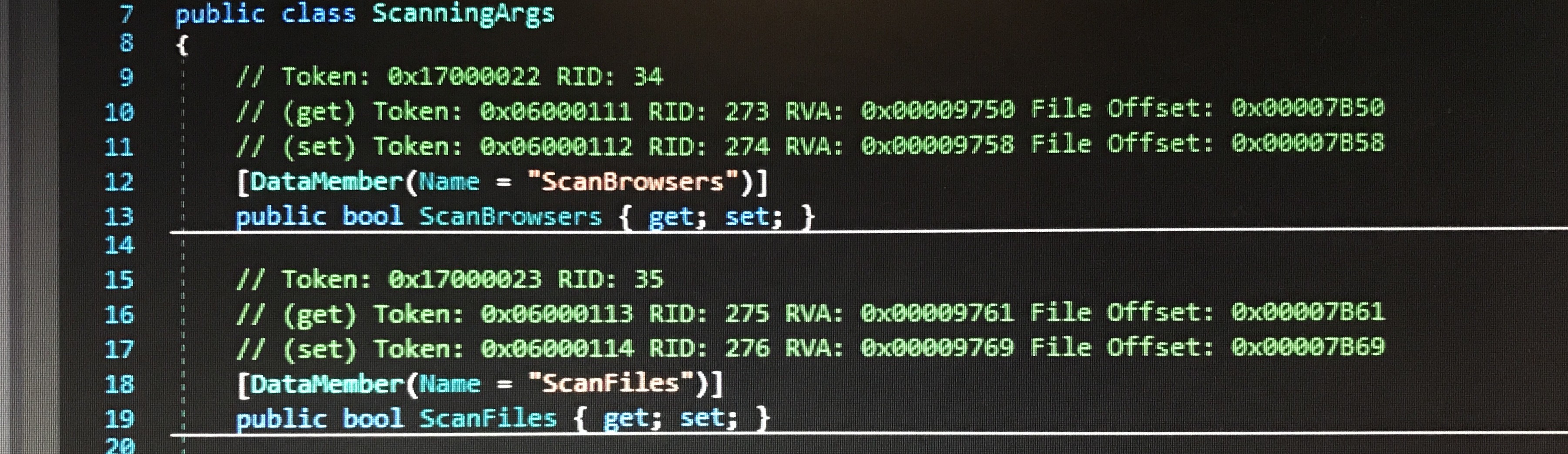
The ScanningArgs class contains parameters corresponding to the different capabilities of the program. This indicates that it might be possible to enable or disable specific scans based on the values of these parameters.
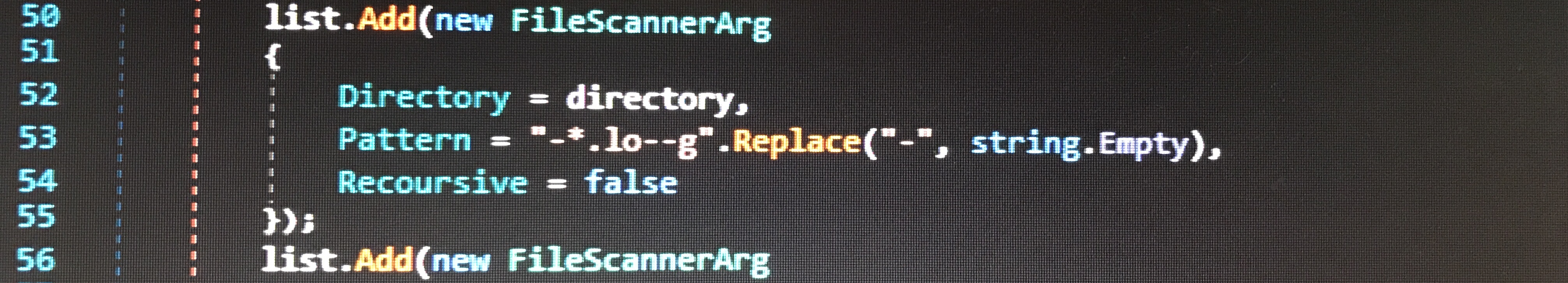
Additionally, a function called SeenBefore checks for the presence of a directory called Yandex\YaAddon in AppData\Local. If the directory does not exist, the program creates it.
Running Tasks
Before performing any scans, the program attepts to determine its own location using the GeoInfo.Get() method. It does so by connecting to several external websites that display one’s own IP address, such as ipinfo.io. The result is checked against the BlockedCountry and BlockedIP parameters of the ScanningArgs. If there is a match, the program immediately exits.
If the program doesn’t exit, the ResultFactory class coordinates most of the actual scanning. First, each parameter of the ScanningArgs object settings is checked. Then, if the setting is enabled, an object is created that performs the subsequent scan and data collection.
Features
-
ScanScreen: The program takes a screenshot and saves it as a PNG file.
-
ScanTelegram: The program scans the
AppData\Roaming\Telegram Desktop\tdatafolder, which stores the user’s Telegram messages. -
ScanBrowsers: The program harvests autofilled logins stored by Chrome. Logins are stored in the
Login Datafolder associated with a user’s profile. They are protected by Windows’ built-inCryptProtectDatafunction, so once one has access to the user’s account, the passwords can easily be decrypted by callingCryptUnprotectData. -
ScanFiles: The program enumerates all drives and makes a list of the names of all files in each one.
-
ScanFTP: The program searches for the
FileZilla\recentservers.xmlandFileZilla\sitemanager.xmlfiles. These files contain saved login credentials from past FTP connections. -
ScanWallets: The program looks for files associated with cryptocurrency wallets. The following files are returned:
.walletfiles inAppData\Roaming\Armory- All files in
AppData\Roaming\atomic - All files in
AppData\Roaming\Coinomi - All files in
AppData\Roaming\Electrum\wallets - All files in
AppData\Roaming\Ethereum\wallets .jsonfiles inAppData\Roaming\Exodus, and all files inAppData\Roaming\Exodus\exodus.wallet- All files in
AppData\Roaming\Guarda - All files in
AppData\Roaming\com.liberty.jaxx - Any files or directories in
AppData\RoamingorAppData\Localcontaining the string “wallet”
-
ScanDiscord: The program searches for Discord tokens using the regex
[A-Za-z\d]{24}\.[\w-]{6}\.[\w-]{27}. -
ScanSteam: The program searches for a directory called
config. Additionally, the program searches for theSteamPathvariable to determine where Steam-related files might be stored. If possible, the program also reads thessfnfile, which is used to authenticate a device to Steam. -
ScanVPN: The program checks the
AppData\Roaming\OpenVPN Connect\profilesandAppData\Local\ProtonVPNdirectories for files containing the stringovpn.